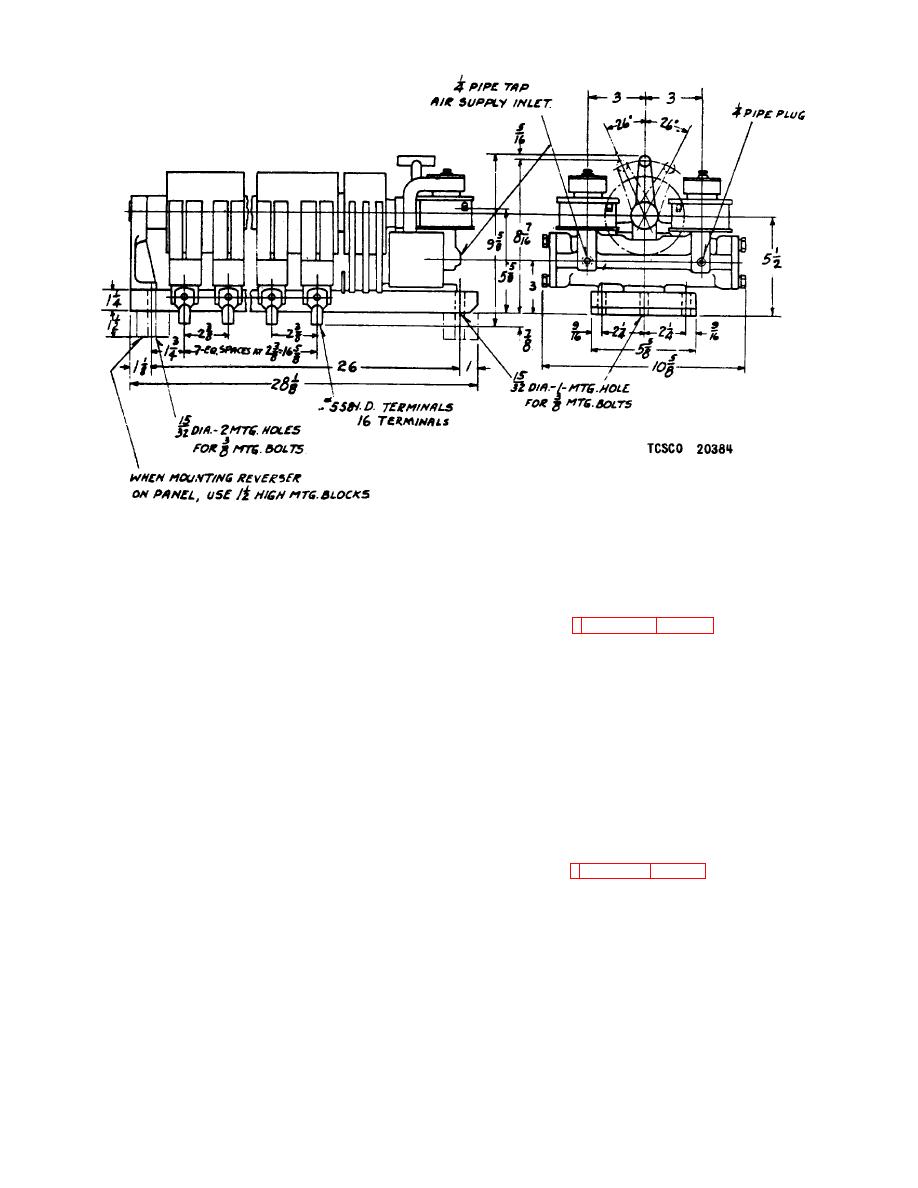
Figure 21. Reverser outline.
being
alternately
energized
or
the admission of air to and the exhaustion
deenergized depending upon the direction
of air from the air-operated cylinders.
of motion necessary.
Magnet valves fall naturally into two
general classifications as to operating
(4) Figures 22 and 23 illustrate the general
principle: namely standard and inverted
principle of magnet valves, using a typical
valves.
cross section of a standard valve, the
chief distinction between the standard and
(2) The standard valve when energized,
inverted valves being that in a standard
admits air from the pressure line through
valve one bushing with two seats (upper
a small port or seat allowing the air to
and lower) and two valve stems are used,
pass through the valve and into the air
while in an inverted valve two bushings
cylinder which actuates the complete
and one floating valve with two faces
piece of apparatus. In this valve the full
actuated by a pushrod and operating
pressure of the air line or reservoir acts
between the bushings are used. The
continuously in the cylinder, as long as
construction of corresponding valve parts
the magnet coil is energized, while
is similar and the following description,
another valve on another seat prevents
therefore, applies to all the valves.
the air from escaping through the magnet
valve exhaust port.
(5) Figures 22 and 23 show the diagrammatic
cross-sectional view of a standard magnet
(3) The inverted valve energized, acts to shut
valve with the operating parts in the
off the air from the supply line and allows
position which they occupy when there is
air to escape from the cylinder through an
no current passing through the coil.
exhaust port in the magnet valve.
Under this condition the spring (a) pushes
Sequence switches usually use both types
the valve (b) up against the seat (c) and
of valves at the same time, due to the
prevents any air from passing from the
opposed direction of travel of the pistons
control air supply to the operating cylinder
in the air cylinder, the magnet valves
50


